Abstract: This paper introduces the design of computer defect detection system based on digital image processing. The system can extract the defect image from the print image and realize the automatic detection of post-print defects on the print surface.
Keywords: defect detection genetic algorithm print
Common post-print defects on the printed surface [1], mainly pinholes, color distortion, ink splashes, black spots, text blur, stains, wrinkles, missing prints, scratches, dislocations and so on. All the defects reflected in the visual effect are inconsistent with the original desired printing effect. The basic principle of the computer-based automatic detection system is to collect a flawless standard print image through a CCD camera and store it in a computer. Then the image to be checked is collected online. Continually comparing the image to be checked with the standard image, detecting an error, obtaining a defect image, and then performing defect classification and measurement statistics on the defect image. This article mainly introduces the method of defect detection in credit card printing.
1 Defect inspection process
The computer defect detection is shown in the flow chart of computer automatic detection. The standard image needs to be input before each kind of print, and it is necessary to continuously collect the image to be checked during normal work.
Since the print product will inevitably undergo translation and rotation in the transmission process, the standard image and the image to be checked are first aligned before the image of the object to be tested is compared with the standard image, ie, the position conversion parameters of both are obtained. Corrected when compared. Here we use a genetic algorithm for image alignment. Strictly speaking, the image should be aligned so that each pixel of the two images can correspond to each other, but this calculation is very large. Because all the pixels in the translation and rotation transform follow the same transformation rules, we select some sampling points on the image to compose the point set S. By obtaining the position transformation parameters of these sampling points, the entire image can be transformed. parameter.
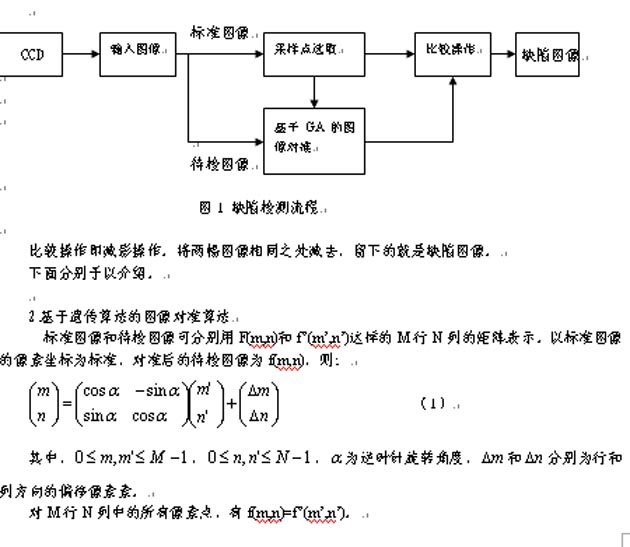
Comparison operation is subtraction operation. Subtracting the two images in the same place will leave a defect image.
The following are introduced separately.
2 Image alignment algorithm based on genetic algorithm

2.3 Choosing the operator The method of using the expected value of better genetic performance [4], that is, (1) According to each individual's fitness value, calculate the expected number of individuals in the group to survive in the next generation.
(2) Select an individual at random and repeat (2) if its survival expectation is less than zero.
(3) If an individual is selected to participate in pairing or crossover, then it subtracts 0.5 from the survival expectation value in the next generation; if it is not involved in pairing or crossover, it is directly copied to the next generation, then its survival expectation in the next generation. Subtract 1.
(4) Turn (2) until a new group is created.
2.4 Genetic operators Crossover operators use single-point crossover, and mutation operators also use basic mutation operators.
2.5 Genetic algorithm flow of image alignment (1) Determine the species size and generate the initial population immediately.
(2) Calculate each individual's fitness value.
(3) According to each individual's fitness value, choose individuals from the population to enter the next child.
(4) Genetic manipulation of individuals in offspring with crossover and mutation probabilities.
(5) Calculate the fitness value of each individual in the offspring.
(6) Exit if conditions are met; otherwise go to (3)
Portable Baby Booster Seat,Baby Feeding Chair,Portable Baby Chair,Kids Study Chair
Zhejiang Lamon Technology Inc. , https://www.chairesbaby.com