The idea of 3D printing can be traced back to the United States in the 19th century. It is also known as 3D printing or rapid prototyping technology. It is a technology that produces 3D solids directly from digital models through material accumulation. According to records, 3D printing technology has been put into practical use in the 1980s and was named "Rapid Prototyping Manufacturing". At present, 3D printing technology has produced comprehensive and profound changes in the fields of product Design, manufacturing process, manufacturing equipment, material preparation, biomedicine, etc., and has become an important symbol of the third industrial revolution, which has received great attention from countries all over the world. China's 3D printing industry started late, the technical level is generally not high, and the industrialization scale is relatively small, but the development momentum is good, and the application in polymer materials is still in the exploration stage.
The principle and characteristics of 3D printing technology
Technical principle
3D printing technology is basically the same as laser forming technology. Simply put, it is to generate 3D solids by layering and superposing and adding materials layer by layer. The reason for calling it a "printer" is based on its technical principle. The layering process of a 3D printer is very similar to that of an inkjet printer. The first is to use the computer to design the 3D model of the required parts, and then according to the process requirements, the model is discrete into a series of ordered units according to certain rules, usually in the Z direction to discrete according to a certain thickness, the original The 3D CAD model becomes a series of layers; then the machining parameters are input according to the contour information of each layer, and then the NC code is automatically generated after the system; finally, a series of layers are formed and automatically connected, and finally A three-dimensional physical entity.
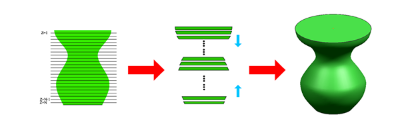
2. Advantages
First, the most direct benefit is to save materials, eliminate the need to remove scraps, improve material utilization, and reduce costs by eliminating production lines;
Second, it can achieve high precision and complexity, in addition to the design on the shape curve;
Third, no longer need traditional tools, fixtures and machine tools or any mold, you can directly generate any shape of parts from computer graphics data;
Fourth, it can automatically, quickly, directly and accurately convert the design in the computer into a model, or even directly manufacture parts or molds, thus effectively shortening the product development cycle;
5. 3D printing can be formed in a few hours. It allows designers and developers to leap from floor plan to solid;
Sixth, it can print out the assembled product, so it greatly reduces the assembly cost. It can even challenge large-scale production methods.
3. Disadvantages
Any product should be functional, and now due to factors such as materials, products manufactured through 3D printing have a question mark in practicality. 1 Strength problem: Although the house and the car can “print†out, but whether it can withstand the wind and rain, whether it can run smoothly on the road is still a problem that must be faced; 2 accuracy problem: due to the layered manufacturing "Effect", although each level is very thin, but at a certain microscopic scale, a first-level "step" with a certain thickness will still be formed. If the surface of the object to be manufactured is a circular arc, it will cause a deviation in accuracy. 3 limitations of materials: At present, the materials used for 3D printers are very limited, no exceptions are gypsum, inorganic powder, photosensitive resin, plastics, etc. The materials that can be applied to 3D printing are also very single, mainly plastic, and printers. Very picky about a single material.
Application of 3D printing technology in polymer materials
1. Types of polymer raw materials
As an important part of 3D printing, materials also play a pivotal role. Currently used 3D printing polymer materials are polyamide, polyester, polycarbonate, polyethylene, polypropylene and ABS. There are many types of oligomers in photocuring embossing, and most of them include urethane acrylate resin, epoxy acrylate resin, polyacrylic resin, and amino acryl resin.
2. Common application process
At present, 3D printing polymer materials technology mainly includes photocuring stereoscopic printing (SLA), fused deposition molding (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), etc. [5].
Light curing stereo printing
Light-cured 3D printing (SLA) works similarly to ink-jet printing. Under the control of digital signals, the liquid photosensitive resin in the working chamber of the nozzle instantly forms droplets. Under pressure, the nozzles are ejected to a specified position and then passed. The ultraviolet light cures the photosensitive resin, and after solidification, it is stacked layer by layer to obtain a formed part. The forming process is as follows: firstly, according to the shape of the cross section of the part, the printing nozzle is controlled to move along the X and Y axes, the solid material is printed on the relevant physical area of ​​the predetermined section, the supporting material is printed on the supporting area, and the curing is performed under the irradiation of ultraviolet light, and then The printing platform is lowered to a certain height along the Z-axis, and the nozzle is then printed and cured to the next layer, so that the layer-by-layer printing is cured until the workpiece is completed, and finally the supporting material in the workpiece is removed to obtain the desired workpiece.
The photocurable 3D printing material is composed of a photocurable solid material and a supporting material, wherein the supporting material can be further divided into a phase change wax supporting material and a photocurable supporting material according to different curing modes thereof. Photocurable support materials, commonly known as photosensitive resins, are composed primarily of oligomers, reactive diluents (active monomers), photoinitiators, and other auxiliaries. Due to the early start of foreign countries, and 3D printers can provide experimental equipment support for the research of photosensitive resin, foreign 3D printing photosensitive resin is more mature. The best foreign companies are currently OBJET in Israel and 3D Systems in the US, which account for the majority of 3D printing photosensitive resin markets. However, these companies use photosensitive resins as their core technology, and the results are rarely announced, and these photosensitive resins are bundled with the photocured 3D printers they produce.
· Special Design : Straight edge flat plate design, simple while graceful. Straight-sided design with large capacity. Effectively prevent soup spillage.
· Stackable & Easy to Clean: These bowls are stackable and DON'T take up a lot of space in your cupboard. Easy to clean, Dishwash top secure. But not use in Microwave.
· Unbreakable & Durable: Melamine is a kind of environmentally friendly materials, does not contain BPA, It won't be shatter like glass and porcelain. It is also perfectly stackable.
Melamine Dinnerware,Burning Stone Ware,New Style Melamine Tableware
Nanjing Demei Melamine Wares Co.,Ltd , https://www.dm-melaminewares.com